ESG
ESG-optimized
Sub-Ecosystem Inheriting
from
the GAPEC’s Attributes
advanced technologies such as AI, blockchain, and AEA further equip members to actualize their sustainability objectives.
Enveloped within the expansive GAPEC Ecosystem, the ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) sub-ecosystem serves as a critical component, establishing sustainable operational frameworks for the whole GAPEC Ecosystem. This involves numerous stakeholders and participants across Macro, Meso, and Micro-scale players. As a constituent of the broader GAPEC ecosystem, the ESG sub-ecosystem absorbs its key characteristics, including its abundant resources within a globular grid and the AEA's XI integration into the IEQBOT. This results in the sustainable market positioning of its members and the facilitation of their 5D+ orientation activities. These activities take into account both the immediate and long-term implications of the members' actions on the environment, social communities, and governance structures.
Balancing economic viability with environmental and social objectives forms the cornerstone of a robust ESG strategy, underscoring the importance of holistic sustainability. This progressive expansion dovetails with the overarching ethos of the GAPEC 's inherent commitment to fostering a sustainable, green future. Moreover, advanced technologies such as blockchain and IEQBOT further equip members with AEA to actualize their sustainability objectives. XCEED Insight (XI) embodies this super-intelligence, derived from professional acumen, creativity, and rich regional culture, strategically deployed to enhance its performance.
An Exploratory Analysis of Sustainability Performance and Corporate Responsibility Indicators Across Multiple Countries
This diagram compares ESG indicators for multiple countries, examining their sustainability performance and corporate responsibility.

Encompassing a multitude of industries and sectors, the ESG sub-ecosystem plays a cardinal role in mitigating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) tribulations. Amid these concerns, the substantial environmental hurdle posed by greenhouse gas emissions commands particular attention. In this vein, constituents of the GAPEC, especially those within the ESG sub-ecosystem, grapple with intensifying demands to curtail their carbon footprint and institutionalize sustainable practices. This necessitates adopting strategies aimed at reducing energy consumption, endorsing renewable energy sources, and integrating circular economy models to minimize waste generation.
Moreover, the diverse nature of the ESG sub-ecosystem, characterized by the operation of its members across heterogeneous regulatory and cultural contexts, poses unique challenges in ESG risk management and upholding consistent standards across the value chain. In response to these challenges, entities within the ESG sub-ecosystem are incumbent to formulate and enforce robust policies and procedures, thereby ensuring they abstain from contributing to negative social or environmental ramifications within any segment of their global value chain. The AEA identifies trends in ESG best practices and uses them to inform sustainable business strategies for Macro, Meso, and Micro-Level players.
Unveiling Macro-Level Sustainable ESG Paradigms Through AEA's Novel Professionalism to Pursue Global Green Initiatives
Macro - Level
Navigating the labyrinthine landscape of the ESG ecosystem necessitates comprehending the roles and strategic objectives of the Macro-Level players. These entities encompass a spectrum of international organizations, transnational corporations, governmental bodies, and civil society entities. An incisive understanding of their operational dynamics, interdependencies, and pressure points is instrumental in orchestrating systemic transformation.
The Paris Agreement, a seminal blueprint in the fight against climate change, mandates a critical recalibration of the operational modalities of nations and organizations. It instigates a tectonic shift towards resilient, low-carbon pathways and serves as a strategic fulcrum for the global battle against climate change. This transformation, underpinned by the principles of regional economic integration and governmental unity, highlights the interconnectedness of sustainable development, societal well-being, and planetary health.
At this juncture, the Augmented Experience Accumulation (AEA) emerges as a potent catalyst in the ESG sub-ecosystem. Harnessing the uncopiable wisdom of XI, AEA empowers and weaponizes the ESG constituents with an INNOTIATIVE approach. This strategy pivots towards the uncharted territory of GAPEC, catalyzing sustainable development trajectories that align with the Paris Agreement's 2030 and 2050 targets.
Moreover, Blowing AEA into the mindware of governments transforms their working culture and values, thereby improving future development plan decision-making and interactions with others without negative trade-offs. Furthermore, the ESG sub-ecosystem, along with AEA, facilitates the development of leadership qualities and managerial skills, allowing countries' leaders to focus more on the growth and prosperity goals of their development plans while ESG aspects are taken care of in the whole system.
AEA and the meritocratic umbrella beyond the GAPEC also upskill governments at the top of the hierarchies, shaping leader countries' behavior, mindset, and habits leveraging in Blowing this behaviorism into their soulware that is multi-angle, multi-targeted, and multi-functional resulting in sustainable economic growth and improved leadership qualities among the global value grid.
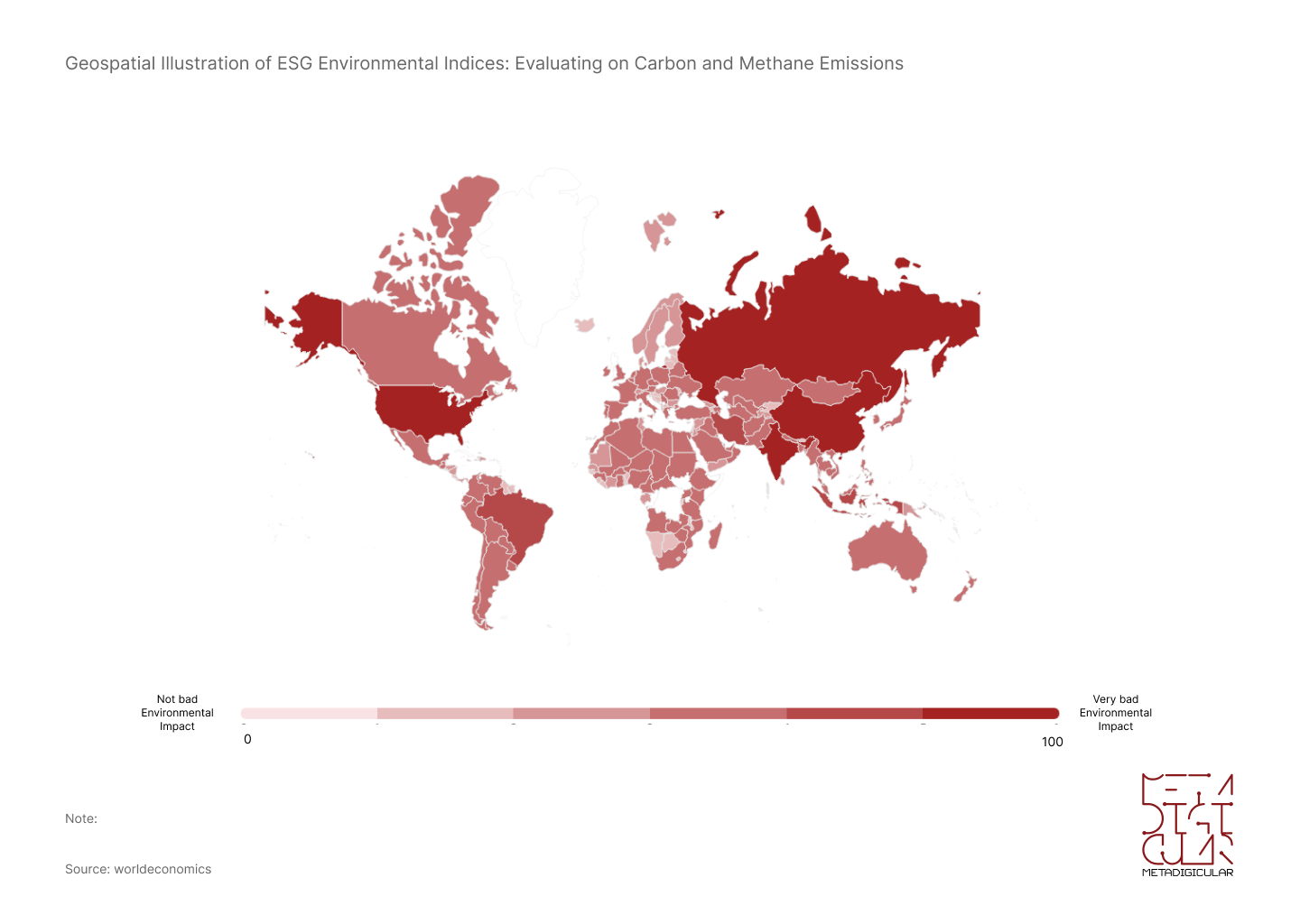
Examining the Macro-Level Environmental Footprint: A Cross-Country Analysis of Emissions, Energy Use, and Waste Management
This innovative geospatial diagram investigates the environmental footprint of Macro-Level players globally by focusing on emission levels, energy usage, and waste management approaches. Highlighting ESG indices, with a special emphasis on Carbon and Methane emissions, the representation utilizes different shades of red to depict the environmental performances of nations. Countries with energy-efficient measures and effective waste management are reflected in lighter shades, whereas those with higher emissions and less sustainable practices are displayed in deeper reds. The striking visual difference accentuates the environmental disparities among global entities and underscores the collective urgency to embrace more sustainable practices, ultimately steering towards a more environmentally responsible future.
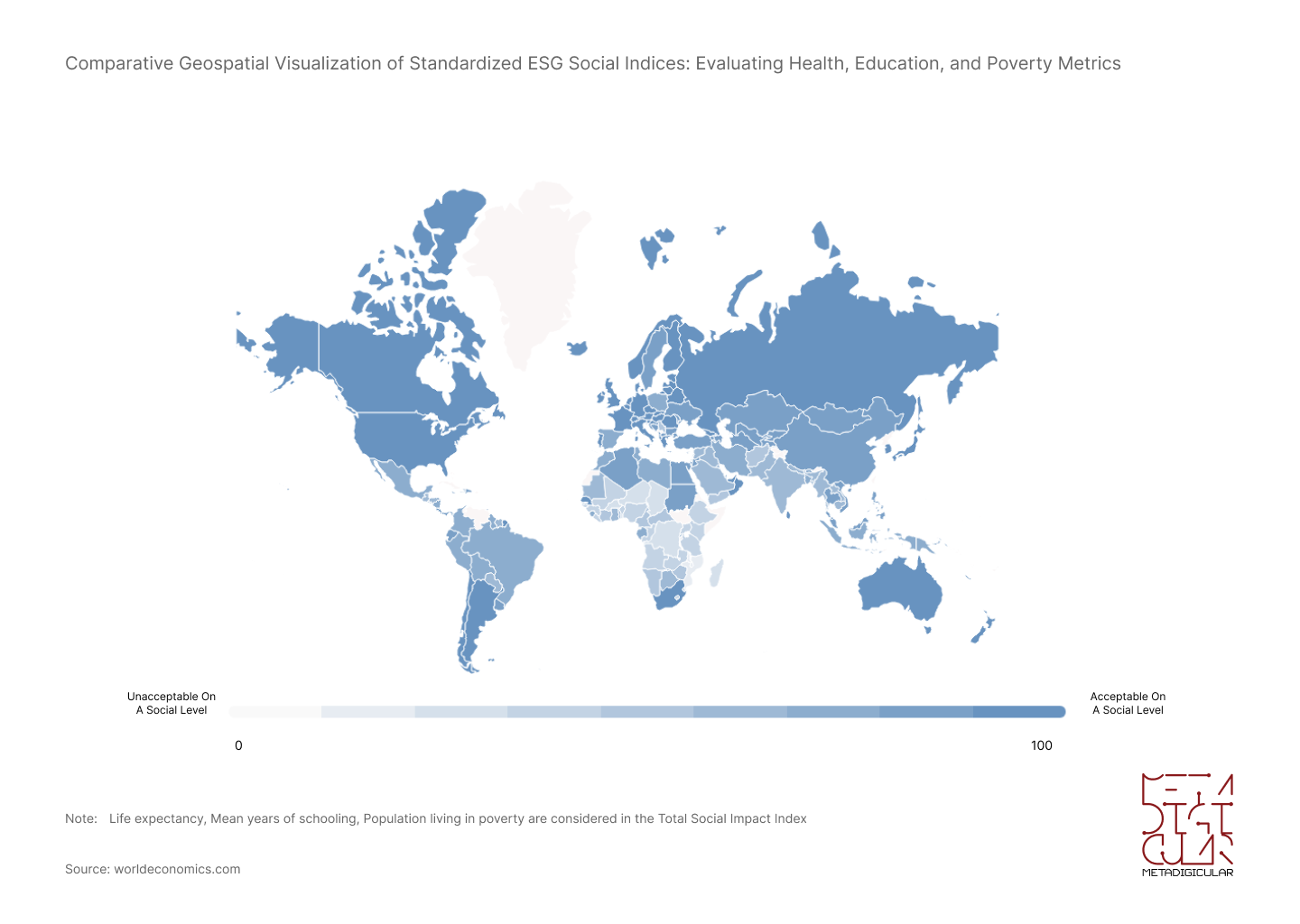
Exploring Social Sustainability Indicators: Analyzing Diversity, Inclusion, and Employee Well-being Across Multiple Countries
This insightful geospatial diagram delves into the realm of social sustainability by analyzing essential indicators such as diversity, inclusion, and employee well-being across an array of nations. The compelling gradient of blue not only emphasizes the differences in social sustainability practices but also reinforces the urgent need for countries worldwide to champion a socially sustainable work culture, thereby promoting a more equitable and humane corporate world.
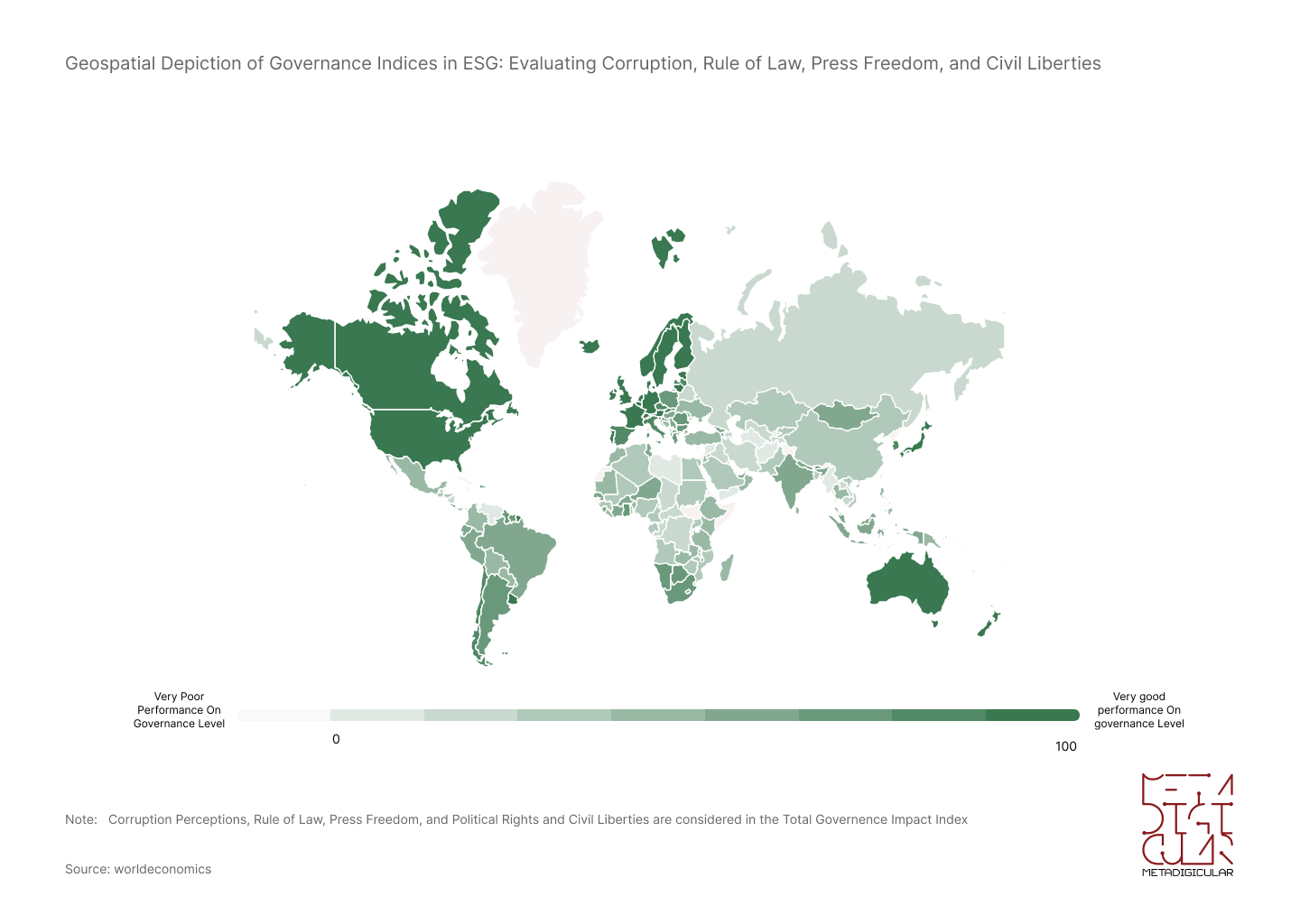
Examining Good Governance Indicators: Analyzing Transparency, Accountability, and Ethics Across Multiple Countries
This compelling geospatial diagram takes a deep dive into the core tenets of good governance, meticulously analyzing transparency, accountability, and ethics across a wide array of nations. The spectrum of green not only underscores the disparities in governance practices but also illuminates the urgent call for nations to adopt enhanced transparency, accountability, and ethical standards, fostering a more just and fair global society.
Economic initiative roads like the Green BRI and the broader concept of green regions and countries are potent harbingers of a sustainable future. The creation of green regions represents a radical reconfiguration of geographical and political spaces under the aegis of sustainability.
Establishing strategic alliances, fortified by resilient governance mechanisms and aimed at a common objective of environmental conservation and sustainable development, is a mandate of the current era. It also maps out a program to transfer clean energy from the energy bases to where the nation's most prosperous provinces and industrial bases are situated through so-called power transmission tunnels. These visionaries encapsulate an ambitious aspiration for infrastructural, economic, and environmental synergy, underpinned by stringent sustainability criteria and innovative financial mechanisms.
To materialize the dream of green regions and alignments, governance bodies must synchronize their policies to meet shared ESG objectives.
This can only materialize when nations align their legal and policy frameworks to maintain a balance between anthropogenic emissions and greenhouse gas sinks. For instance, nations should progress towards a net-zero target as a part of the environmental facet of ESG to mitigate climate change impacts. During this structural and economic transition, it's crucial to ensure justice, particularly for socials such as workers in high-carbon industries. The costs and benefits of transitioning to a net-zero emissions economy must be equitably distributed. This necessitates investments in carbon removal techniques as well as sustainable finance instruments.
A variety of financial instruments are designed to support projects with positive ESG impact, collectively known as sustainable finance instruments. These include sovereign green and sustainability bonds, sovereign blue, green, and climate bonds, carbon credits/cap and trade systems, development bank financing, green quantitative easing (green QE), supranational climate transition bonds, national development banks (NDBs), international climate funds, resilience bonds, environmental impact bonds (EIBs), sustainable linked loans (SLLs) at the sovereign level.
These financial instruments necessitate an enabling legal and regulatory framework and clear, ambitious, and achievable environmental targets that attract investors. Equally vital is the capacity to develop and manage green projects, underlining the importance of knowledge and skills.

A strategic approach to sustainable development demands a profound understanding of the inherent challenges and potential solutions. Here, the ESG sub-ecosystem of GAPEC, with its holistic 5D+ integrated system and augmented wisdom, plays a crucial role. It doesn't only facilitate the process but also offers capacity-building opportunities to government officials, promotes engagement with international organizations or experts, and fosters partnerships with development banks or other national-level institutions.
The credibility of GAPEC instills confidence in investors that funds will be utilized as promised and prevent greenwashing and any other performance or technological risks.
The diversity of players and entities within the GAPEC ensures the involvement of all relevant stakeholders in developing and implementing green finance.
Moreover, the ecosystem orchestrates partnerships, competitions, collaborations, and alliances with international institutions, such as the World Bank or regional development banks. These partnerships can provide the technical assistance and cutting-edge technologies required to transition towards a sustainable economy, along with funding to develop green finance sectors and incentives for green investments.
Participation in this DIGICULAR Metanomy offers a strong element of financial inclusion, capacity building, and financing investments leading towards sustainable development. It also reduces the financial risks associated with sustainability issues.
The wisdom and methodologies of AEA have generated unique, high-value shared proposition hubs in GAPEC.
In the complex ESG sub-ecosystem, diversification is a key. It fosters resilience and robustness amidst evolving global challenges without undue resource expenditure. Nations can adapt to changing circumstances, mitigate systemic risks, and contribute to a more sustainable global future by leveraging diverse sustainable practices. The wisdom and methodologies of AEA have generated unique, high-value shared proposition hubs in GAPEC. These featured insights of the ESG sub-ecosystem weaponized with AEA, address and solve customized special challenges and barriers while fostering stability for members and promoting global sustainability.
Adherence to the United Nations’ ESG agreements, promotion of an inclusive green value chain, and enabling nations to contribute to the green global value grid are essential in the global sustainability context. Countries failing to align with these guidelines may find themselves self-sanctioned and disconnected from global sustainable development initiatives. This isolation can lead to economic stagnation, compromised societal well-being, and increased environmental degradation.
The ESG sub-ecosystem compensates countries by minimizing emissions and environmental impacts from challenging sectors, such as heavy industries and manufacturing, with an emphasis on sustainable positioning. By fostering the development of green industries, it plays a crucial role in transitioning to a sustainable economy. Through the GAPEC, facilitated by XI's rich cultural understanding and wisdom, countries can shift towards a sustainable global future without geopolitical tension.

The DIGICULAR Metanomy system's integration of blockchain technology into the GAPEC Ecosystem including all its sub-ecosystems, such as ESG, enhances transparency. This effectively prevents potential debt traps and other adverse outcomes, often leading to the dissolution of international alliances and agreements. By leveraging blockchain's decentralized and immutable nature for record-keeping within a smart ledger scheme, nations can ensure accuracy and transparency. Simultaneously, centralized governance provides credibility and operational efficiency, facilitating the development of fair and sustainable international collaborations.
In the ESG sub-ecosystem, complex expertise augmented wisdom with exceptional professionalism, XCEED Insight (XI), which is a result of years of working on an international level with diverse countries, where ethical practices, value creation, and equal respect for everyone are top priorities that members of the ecosystem adhere to, is utilized to tackle the issue of discrimination and minimize geographical disparity. This is achieved through the use of cutting-edge data-driven technological tools. The significant presence of the WORLDISATION hyper flow value of GAPEC in the ESG sub-ecosystem transformative initiative enhances transcontinental connectivity and cooperation, the merger of governments, resulting in regional alliances, the unification of borders, and binding countries that represent a substantial portion of the world's GDP. It catalyzes the DIGICULAR Metanomy system and green trade expansion, bridging gaps between nations and circular economy.
The WORLDISATION framework, within the ESG sub-ecosystem, is strategically built around facilitating ESG policy harmonization, enhancing sustainable infrastructure connectivity, promoting unobstructed, sustainable green trade, and encouraging green economy integration, which improves human well-being and social equity while significantly reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities. It also focuses on conducting effective, steady super national trade, operations, and green investments, backed by the World Bank or the International Finance Corporation. These pillars encapsulate a comprehensive approach to fostering international ESG cooperation and driving green economic 5D+ integration within the Globular and Curvycular Economy. The orchestrator of the GAPEC manages this strategic approach, which promises a future where sustainable development, societal well-being, and planetary health are interconnected and mutually reinforcing.
AEA’s INNOTIATIVE Trailblazing Framework for Mezzo-Level ESG Futurist Paragon
Mezzo - Level
Undeniably, embracing ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) practices positively impacts a business's or organization's maturity, growth, and overall success. By addressing environmental, social, and governance factors, businesses can attract customers, investors, and talent, mitigate risks, and seize emerging market opportunities. Incorporating ESG considerations into business strategies contributes to long-term value creation, resilience, and competitiveness, ultimately driving business success.
It is evident that ESG data insights are revolutionizing business and societal practices, heralding the emergence of sustainable enterprises. As a result, business sustainability has become a paramount trend, significantly impacting companies' market competitiveness and, ultimately, their survival.
In this era of data-driven decision-making, the ESG sub-ecosystem offers its members AEA, IEQBOT, and blockchain-based solutions that provide highly professional and precise insights. These insights enable Mezzo-Level players of the ecosystem to manage climate and environmental risks effectively, optimize asset performance and resource utilization, promote decarbonization, and nurture sustainable supply chains. Ordinarily, business leaders heavily capitalize on potential ESG reports.
Simultaneously, members gain ESG portfolios with independent intellectual property rights through the AEA evaluation, assessment, and analysis, empowered by the unparalleled wisdom of XI. These technological capabilities weaponized with the augmented wisdom of XI serve as critical drivers for business maturity development, providing a competitive advantage to enterprises within the ecosystem using the cutting-edge, data-driven technology and uncopiable expertise wisdom of the AEA.
With this assessment, harmonizing with the meritocracy of GAPEC, corporations find optimal positioning within the ecosystem, valued based on their abilities and potential. This positioning aids in accelerating sustainability progress from Z to A, bypassing the ordinarily prolonged process. This support stems from the unique, high shared-value hubs of the GAPEC, which provide ESG strategy and ecosystem management, finance, and investment portfolios. As businesses find their optimal position within the interconnected ESG sub-ecosystem, new Mezzo-Level members begin to understand and Know Their Ecosystem, leveraging behaviorism, habit creation, and interaction thinking.
However, the path toward corporate sustainability is laden with numerous obstacles. A glaring lack of tools, insights, and expertise often leaves businesses inadequately equipped to formulate and implement a robust sustainability vision and framework. This lack of preparedness exposes companies to considerable risk, which affects their global market presence.
The ESG sub-ecosystem, a component of the GAPEC Ecosystem, introduces a unique DIGICULAR Metanomy system that leverages the collective wisdom of its members to mitigate these challenges, facilitates business upskilling, preparing them for future sustainability challenges, and unlock more enormous environmental challenges into opportunities.
Furthermore, members' interdependence promotes a shared commitment to sustainability and encourages investment in green enterprises.

Moreover, IEQBOT designs customized Augmented Experience Design Packages for businesses. These personalized and innovative strategies, like business process reengineering (BPR), help gain investor confidence, earn customer loyalty, reduce operating costs, and improve both asset management and financial performance. Moreover, AEA promotes ESG practices such as using energy-efficient software, developing green technology, and using data analytics to track and improve ESG performance and transformation from the GAPEC's initial unique high shared value hub. This approach propels businesses to higher-level positions that exceed their potential. Furthermore, it prepares businesses for future sustainability challenges and immense ecosystem opportunities compared to those within the market they currently inhabit. With meritocracy positioning, businesses begin to boost their existing potential through the Blowing of AEA into their mindware and soulware, and then the growth process continues, expanding along with them.
Unveiling Preemptive Strategies and Preventive Solutions to Counter ESG Challenges within the GAPEC's Mezzo-Level Sub-ecosystem
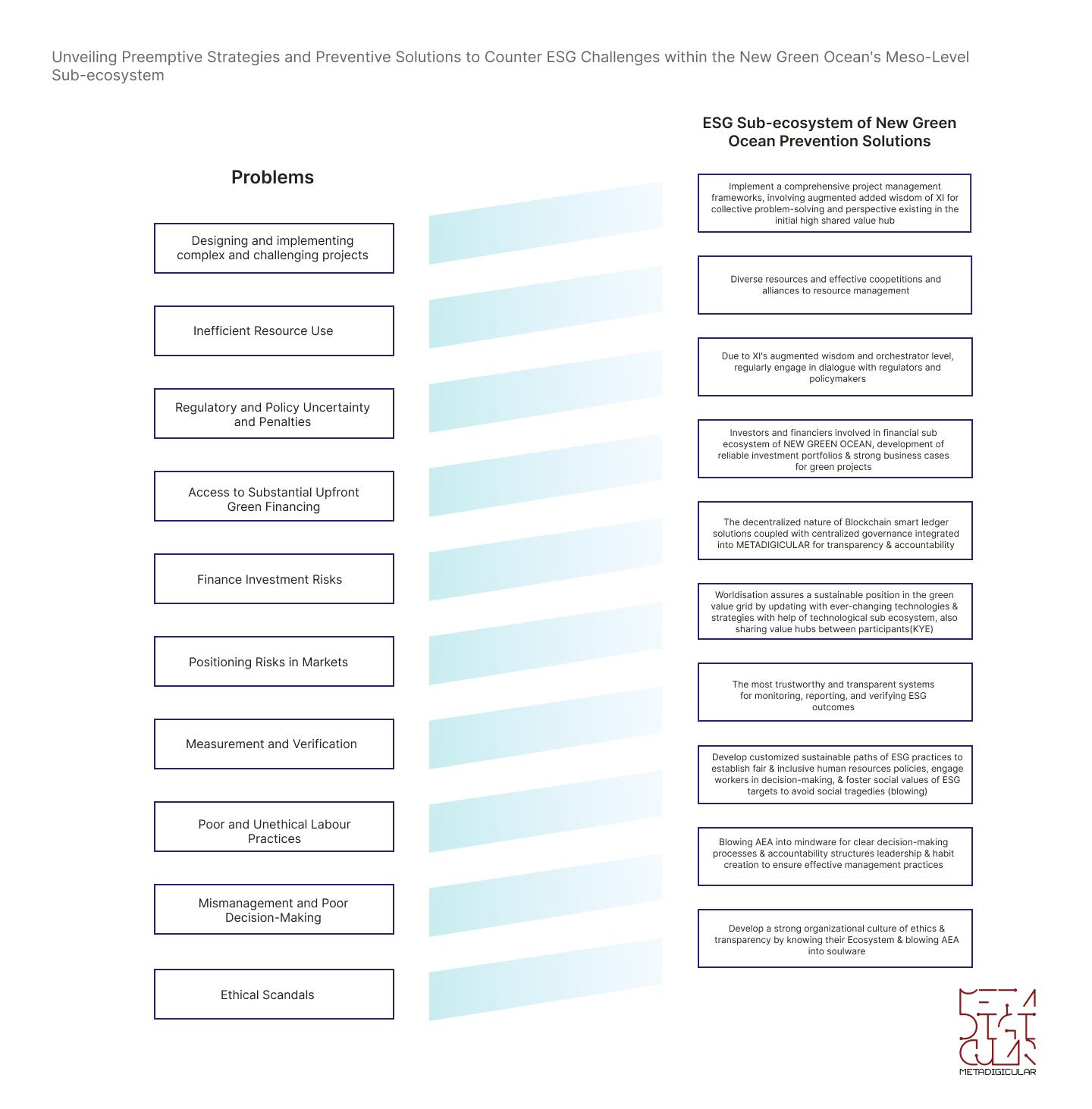
AEA, with its XI wisdom, identifies coopetition for businesses, such as green partnerships and multinational companies, green business models, and innovations in financing and investment (green tokens, green funds) within a 5D+ approach in the Globular and Curvycular Economy. By forming partnerships with sustainable businesses globally and aligning their operations with international sustainability efforts and initiatives, businesses also contribute to constructing a network where sustainable practices create and exchange across borders, which leads to a green global value grid.

This ensures access to capital, as investors are increasingly interested in companies that prioritize ESG factors, and the Financial sub-ecosystem of GAPEC also includes top-notch investors and financiers. However, implementing sustainable practices often requires considerable upfront investments, which can serve as a deterrent. Moreover, systemic inertia, characterized by a short-sighted focus on immediate benefits over long-term sustainability, impedes the pace of sustainability adoption. By adopting ESG principles and demonstrating a commitment to sustainability, businesses can access capital from investors who prioritize sustainable investments.
Innovation opportunities arise as the ESG sub-ecosystem emphasizes collaboration, shared values, and problem-solving, leading to innovative opportunities for businesses along with its Technological sub-ecosystem. By collaborating with other stakeholders, businesses can identify new solutions, technologies, and business models to help them achieve their sustainability goals and goals for diversity and inclusion by implementing supportive policies, providing model inclusive behavior, and promoting a workplace culture where all employees feel safe and valued, thereby benefiting from diverse perspectives and potentially increase profitability. This shapes the collective wisdom of each member, avoiding social tragedies and revolutionizing the growth process.
Green entrepreneurs have the opportunity to transform environmental challenges into economically sound businesses by linking these challenges with potential needs and market demands. In addition to aiding investors in identifying firms expected to perform well on future ESG criteria , the AGI within IEQBOT, guided by XI in its analysis, helps predict the performance of ESG factors. This allows investors to find optimal investments that align with their expectations of investing in companies meeting their standards, along with the minimization of investment risk. As risks are reduced and green investment opportunities are presented, more Mezzo-Level players of the ESG sub-ecosystem adopt sustainable practices, leading to more effective coopetition between them, as well as wealth creation without compromises and trade-offs.
Aside, businesses are increasingly finding themselves at the nexus of environmental crises and social complexities and challenges. However, in the ESG sub-ecosystem, AEA weaponizes participants and cooperates to harness these hurdles as a unique landscape ripe with opportunities, also turning the tide and making them pioneer sustainable solutions. So, the investment cooperation and individual investors of the Financial sub-ecosystem become more willing to invest in these new green investing opportunities. This will strengthen currently operating businesses, positioning them more stably and enabling them to establish better, more extensive, and more successful collaborations.
Achieving sustainability is the transformation of conventional industry and production patterns into green, eco-efficient systems. AEA arms businesses to adopt sustainable technologies and practices easily and in the most accessible way that minimizes waste reduces emissions, and enhances resource efficiency by integrating green design principles, and engagement initiatives, from initial high shared value hub into product development and also regular training with the newest knowledge in Academical sub-ecosystem, which dramatically reduce environmental impacts across their product lifecycle. In GAPEC, businesses and companies are also urged to cultivate a culture of sustainability within their workforce by Knowing Their Ecosystem and AEA manner, which is Blown into their soulware.
so across this whole business sustainability maturity progress, the sustainable era that exists within the ESG ecosystem, and other sub-ecosystems of GAPEC is not limited to Mezzo-Level's own operations but extends across their supply chain. Through this Blowing AEA into their soulware, in this case, such as the implementation of green procurement policies, businesses can consciously choose suppliers who demonstrate a strong commitment to sustainability. Also, the smart ledger scheme of GAPEC emphasizes transparency and accountability throughout the supply chain and promotes an environment of mutual trust and shared responsibility. IEQBOT, by utilizing high-level human capital and artificial intelligence and using the latest technology to analyze market data and predict price changes, enables conveying AEA to help market participants adhere to emissions caps by aiding traders in understanding the cap and trade situation of various businesses within the industry as a whole. Engaging stakeholders in this process ensures alignment with their expectations and enables businesses to gain valuable insights for further improvement, including safer investments, a more trustworthy and respectable brand, and generally improved corporate reputations. This agreement benefits both parties, creating a win-win situation, while being at the forefront of driving the sustainable economy of the future.
Blowing AEA into the mindware and soulware of micro-Level, embracing the meritocracy, preventing trade-off
Micro - Level
Through members' presence, participation, involvement, and engagement in The GAPEC Ecosystem weaponized by AEA, individuals’ mindsets will reshape. AEA logically and intelligently equips its mindset to result in better decision-making for all parties involved in the GAPEC Ecosystem weaponized by AEA. By blowing AEA into their mind-ware, AEA shapes members' behavior, mindset, and habits by creating a customized path with significant multi-angle, multi-targeted, and multi-functional values, which intervenes with their soulware.
By leveraging behaviorism, habit creation, and interaction thinking, members can increase their awareness, wisdom, and superintelligence strategies through the resources, values, solutions, and proper preventive measures provided by this initiative's ecosystem. Through this process, members can add more value to the existing hub of shared high values in the GAPEC Ecosystem.
By helping members understand and (KYE)know their ecosystem, they are better equipped to contribute to it in meaningful ways. This understanding and contribution, combined with their evaluated potential and assets, leads to the emergence of a meritocracy where members are valued based on their abilities and contributions to the ecosystem.
As they continue to engage with the ecosystem, their behavior shapes and reinforces positive mindware and soulware. This holistic approach to knowing the ecosystem and engaging with is critical to creating a sustainable and effective meritocracy. Participation in this ecosystem enables individuals to achieve their goals all about the ecosystem, right to the point in a fast-paced era from the z point instead of driving through this long a-to-z path in the current market, resources, and financial sources conditions without meritocracy.
Creating change in the social aspects of ESG can change the social aspects of the world.
By integrating the knowledge and experience accumulated by highly qualified experts at the operational and cooperative levels, AEA can design, execute, and develop innovative significant changes based on mechanism dataism and data-driven strategy, transforming not just the global economy, but also the global value chain, and the effects of implementing and developing innovative solutions like smart ledgers and decentralized management.
Green behaviorism and habit creation in the weaponized ESG sub-ecosystem inherent in The GAPEC Ecosystem has on the members preventing trade-offs between social progress and economic efficiency by raising awareness about environmental and social impacts, resource and feedstock availability, health and safety risks, innovation and technology, and the circular economy to move toward sustainability and invest more in green products and businesses, reducing the cognitive effort needed to continue engaging in them. Creating share points in a dataset (galaxy) to present AEA blowing into mind-ware and soul-ware, creates the behavior routine that customers are deeply in need of the services that the ecosystem provides. Behaviorism and interaction thinking generate a wave of high values, which they add to and share with other ecosystem members as they interact.
AEA reshaping individuals' mindware and soulware to renovate and create new thoughts for businesses. As the Imminent occurrences of 5th industrial technological, ideological revolution rely on mindware, and soulware along with meritocracy, opening the gate for a new industrial revolution and those who join the flow will overtake others, preventing this trade-off in the path of sustainability to utilize 100 percent of resources efficiently and reach pick potentials. Turning environmental challenges into business opportunities. Affiliative production creation refers to the process of providing individuals with resources and support to help them develop their skills, reach their full potential, and bring their creative ideas to life.
This can involve providing access to resources such as training programs, funding, mentorship, and networking opportunities, to enable individuals to grow and succeed in their chosen fields avoiding sticking in the seizing and freezing, leading them to rethink and unlearn to the growth.
Michael Porter is a Harvard Business School professor who suggests creating shared value (CSV) to solve societal challenges while expanding economic value.
The best way of earning money is through value creation and value sharing.
This approach provides members with a lot of value and success, resulting in the emergence of meritocracy. In exchange, AEA will establish a special habit creation by behaviorism to further promote the overall sustainability of the ecosystem.
AEA preventing the social tragedy of job loss caused by AI
AI is one of the most impactful current technologies. Its innovative solutions are in high demand, but it is also reducing job opportunities for less educated individuals, resulting in a negative impact on lower-wage jobs, faced them social tragedies. The need to resolve this crisis and the concern over job loss highlights the importance of AEA, which is built on super high-level human capital and professionals. There are several ways in which AEA creates opportunities for individuals to prevent social tragedies such as job loss due to AI.
Creating new jobs, the Impact of AEA on human resources
AEA offers individualized, personalized, and customized Augmented Experience Design solutions, even for individuals, to address major social issues. By providing education, skill development, professionalization, scaling up, and leveling up of human resources, AEA aims to help individuals have more time, earn more money, reduce stress, and develop the mindset to become thought leaders in technology. As knowledge grows, the impact of AEA on social sustainability increases, and this also benefits businesses and management. AEA creates high scalability for the members of the ecosystem. Moreover, provides wisdom for individuals in the organizations to grow and expand their potential. AEA will decrease this social tragedy sharply and revolutionize the process of growth for hard-working individuals and businesses.
Through members' presence, participation, involvement, and engagement in The GAPEC Ecosystem weaponized by AEA, the joy of all advantages of the ecosystem bringing ESG awareness and staying informed about new developments in the field through professional associations for the member, cause new jobs as ESG local expert form to facilitate regional ESG transformation with local knowledge.
Allowing for the upskilling and reskilling of current HR capital to sustain businesses in a new directional target.
Augmented Experience Accumulation could enrich businesses with deep knowledge, allowing for the upskilling of current HR capital to sustain businesses in new directional targets. This is achieved by gaining insight via the GAPEC Ecosystem, which aims to resolve the social and tragic challenges of ESG and convert them into social reinforcement positioning.
The upskilling that occurs for businesses and individuals is not academic like universities, but rather more practical. This is due to the ecosystem being filled with talented resources that have operational potential, along with access to various tools. AEA's mission is to help businesses overcome the challenges posed by all social aspects of ESG. This mission is the result of a rich history of highly skilled professionals who have operated at both operational and managerial levels in a wide range of industries.
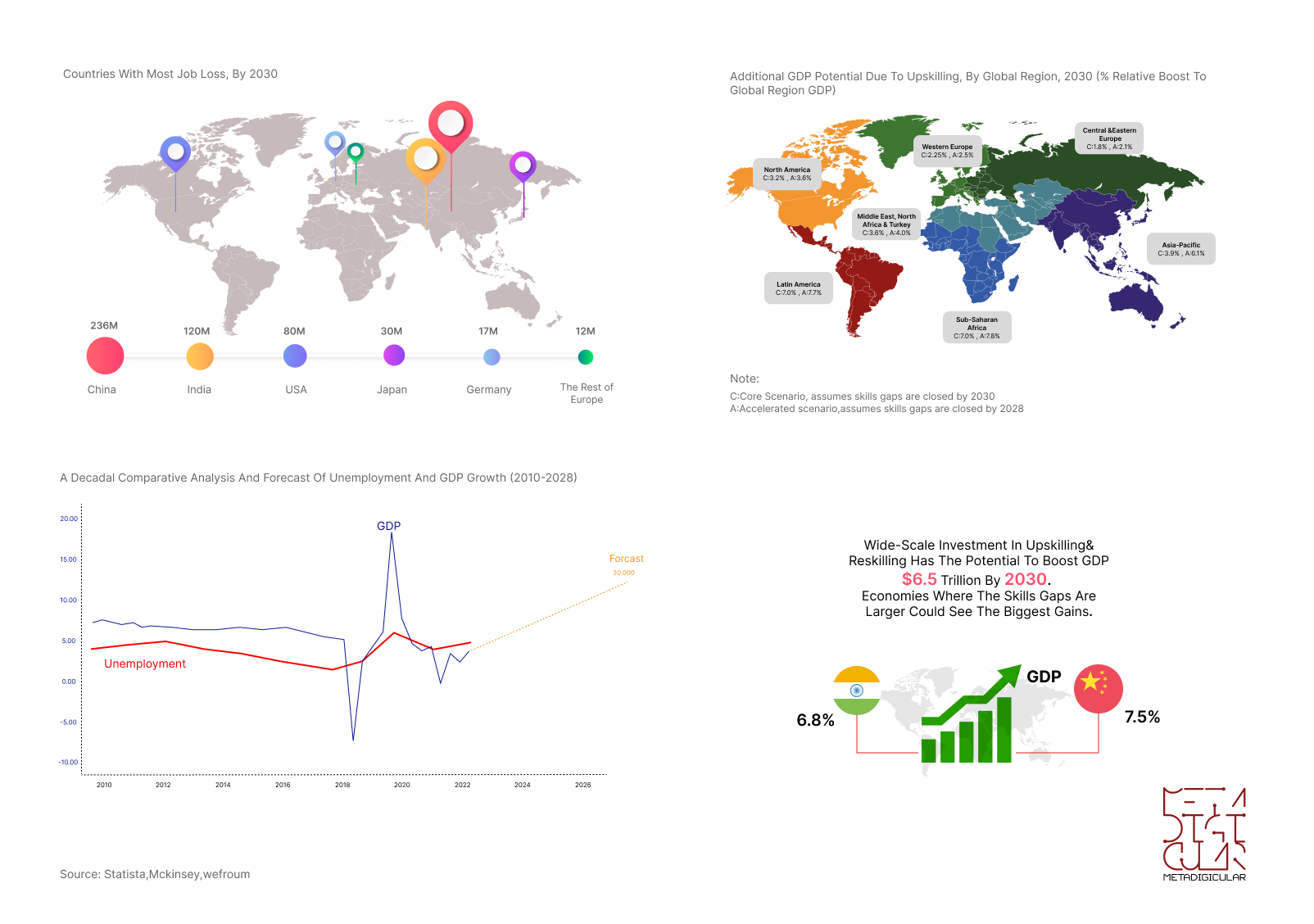
Wide-scale investment in upskilling and reskilling has the potential to boost GDP by $6.5 trillion, despite the forecast of 236 million job losses in China by 2030
The future of work has already arrived in many industries, making the skills gap in the world's 3 billion-strong workforce one of the most urgent challenges for governments, businesses, and workers alike.